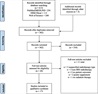
Objective The following research question was asked: In patients with vestibular schwannoma (VS) that underwent stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) and cochlear implantation, were improvements in hearing function observed, and what was the cochlear implant (CI) failure rate of in these patients? Data Sources PubMed/Medline, CINAHL (EBSCOhost), and Web of Science articles without restrictions on publication dates were searched. Study Selection Inclusion criteria required that the article was a report, a series, or a retrospective review with individual case data available. Non-English articles were excluded. Inclusion criteria required that patients were with VS and underwent subsequent SRS and cochlear implantation. Patients receiving microsurgery or stereotactic radiotherapy on the ipsilateral ear were excluded from this study. Data Extraction Included studies were evaluated using full-text evaluation, and data on study characteristics (author names, gender), clinical data (syndromic information, SRS modality), hearing outcomes, and device failure were extracted. Data Synthesis Means and averages were obtained for all continuous variables. Percentages were ascertained for all categorical variables. Conclusions The majority of patients undergoing CI placement in VS treated with SRS achieved open-set speech perception (79.2%) or environmental sound awareness (6.8%). Twelve implants (20.3%) failed. Three patterns were associated with failure: 1) immediate-onset failure, 2) initial benefit with delayed failure, 3) poor local control with device explantation.
No comments:
Post a Comment