Note: A drogue is a sea anchor resisting drifting speed.
The best context for understanding decadal temperature changes comes from the world's sea surface temperatures (SST), for several reasons:
- The ocean covers 71% of the globe and drives average temperatures;
- SSTs have a constant water content, (unlike air temperatures), so give a better reading of heat content variations;
- A major El Nino was the dominant climate feature in recent years.
HadSST is generally regarded as the best of the global SST data sets, and so the temperature story here comes from that source, the latest version being HadSST3. More on what distinguishes HadSST3 from other SST products at the end.
The Current Context
The chart below shows SST monthly anomalies as reported in HadSST3 starting in 2015 through December 2018.
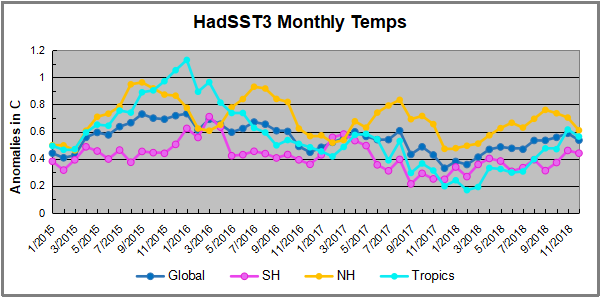
A global cooling pattern is seen clearly in the Tropics since its peak in 2016, joined by NH and SH cycling downward since 2016. 2018 started with slow warming after the low point of December 2017, led by steadily rising NH, which peaked in September and cooled the last 3 months. The Tropics have risen steadily since July, and along with a bump in SH pulled the Global anomaly up slightly, peaking in November.
The December Global anomaly is higher than 2017 but still lower than 2015. Similarly, NH, SH and the Tropics are all slightly higher than 2017, but still lower than 12/2015. The rise in the Tropics is likely due to the weak El Nino, maybe also affecting the SH, but has now backed down.
Note that higher temps in 2015 and 2016 were first of all due to a sharp rise in Tropical SST, beginning in March 2015, peaking in January 2016, and steadily declining back below its beginning level. Secondly, the Northern Hemisphere added three bumps on the shoulders of Tropical warming, with peaks in August of each year. A fourth NH bump was lower and peaked in September 2018. Also, note that the global release of heat was not dramatic, due to the Southern Hemisphere offsetting the Northern one.
The annual SSTs for the last four years are as follows:
| Annual SSTs | Global | NH | SH | Tropics |
| 2014 | 0.477 | 0.617 | 0.335 | 0.451 |
| 2015 | 0.592 | 0.737 | 0.425 | 0.717 |
| 2016 | 0.613 | 0.746 | 0.486 | 0.708 |
| 2017 | 0.505 | 0.650 | 0.385 | 0.424 |
| 2018 | 0.480 | 0.620 | 0.362 | 0.369 |
2018 annual average SSTs across the regions are close to 2015, slightly higher in SH and much lower in the Tropics. The SST rise from the global ocean was remarkable, peaking in 2016, higher than 2011 by 0.32C.
A longer view of SSTs
The graph below is noisy, but the density is needed to see the seasonal patterns in the oceanic fluctuations. Previous posts focused on the rise and fall of the last El Nino starting in 2015. This post adds a longer view, encompassing the significant 1998 El Nino and since. The color schemes are retained for Global, Tropics, NH and SH anomalies. Despite the longer time frame, I have kept the monthly data (rather than yearly averages) because of interesting shifts between January and July.
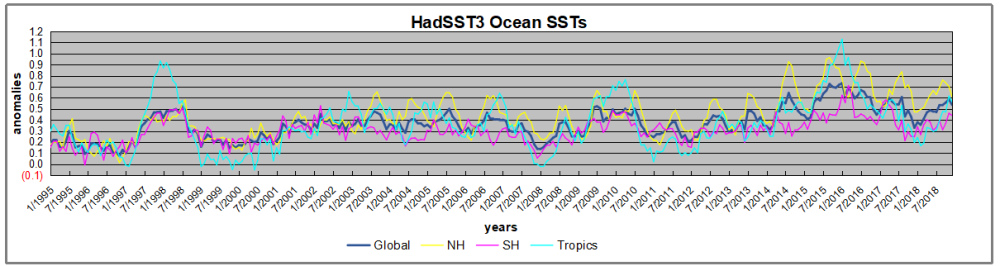 1995 is a reasonable starting point prior to the first El Nino. The sharp Tropical rise peaking in 1998 is dominant in the record, starting Jan. '97 to pull up SSTs uniformly before returning to the same level Jan. '99. For the next 2 years, the Tropics stayed down, and the world's oceans held steady around 0.2C above 1961 to 1990 average.
1995 is a reasonable starting point prior to the first El Nino. The sharp Tropical rise peaking in 1998 is dominant in the record, starting Jan. '97 to pull up SSTs uniformly before returning to the same level Jan. '99. For the next 2 years, the Tropics stayed down, and the world's oceans held steady around 0.2C above 1961 to 1990 average.
Then comes a steady rise over two years to a lesser peak Jan. 2003, but again uniformly pulling all oceans up around 0.4C. Something changes at this point, with more hemispheric divergence than before. Over the 4 years until Jan 2007, the Tropics go through ups and downs, NH a series of ups and SH mostly downs. As a result the Global average fluctuates around that same 0.4C, which also turns out to be the average for the entire record since 1995.
2007 stands out with a sharp drop in temperatures so that Jan.08 matches the low in Jan. '99, but starting from a lower high. The oceans all decline as well, until temps build peaking in 2010.
Now again a different pattern appears. The Tropics cool sharply to Jan 11, then rise steadily for 4 years to Jan 15, at which point the most recent major El Nino takes off. But this time in contrast to '97-'99, the Northern Hemisphere produces peaks every summer pulling up the Global average. In fact, these NH peaks appear every July starting in 2003, growing stronger to produce 3 massive highs in 2014, 15 and 16. NH July 2017 was only slightly lower, and a fifth NH peak still lower in Sept. 2018. Note also that starting in 2014 SH plays a moderating role, offsetting the NH warming pulses. (Note: these are high anomalies on top of the highest absolute temps in the NH.)
What to make of all this? The patterns suggest that in addition to El Ninos in the Pacific driving the Tropic SSTs, something else is going on in the NH. The obvious culprit is the North Atlantic, since I have seen this sort of pulsing before. After reading some papers by David Dilley, I confirmed his observation of Atlantic pulses into the Arctic every 8 to 10 years.
But the peaks coming nearly every summer in HadSST require a different picture. Let's look at August, the hottest month in the North Atlantic from the Kaplan dataset.
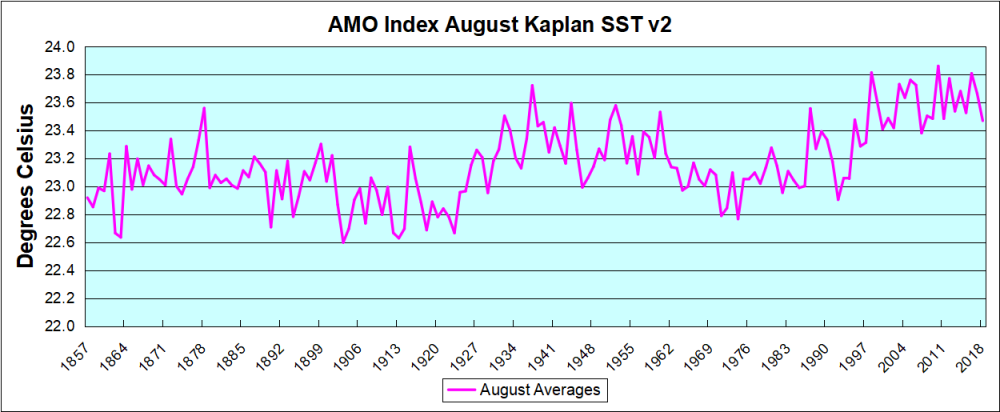
The AMO Index is from from Kaplan SST v2, the unaltered and not detrended dataset. By definition, the data are monthly average SSTs interpolated to a 5×5 grid over the North Atlantic basically 0 to 70N. The graph shows warming began after 1992 up to 1998, with a series of matching years since. Because the N. Atlantic has partnered with the Pacific ENSO recently, let's take a closer look at some AMO years in the last 2 decades.
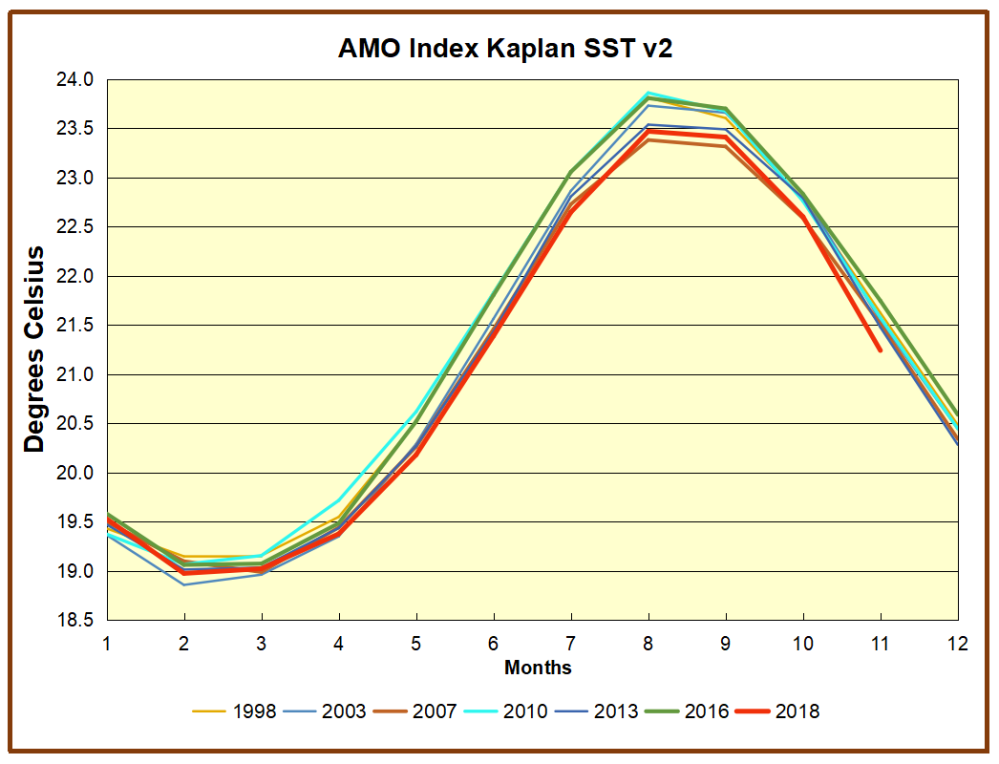
This graph shows monthly AMO temps for some important years. The Peak years were 1998, 2010 and 2016, with the latter emphasized as the most recent. The other years show lesser warming, with 2007 emphasized as the coolest in the last 20 years. Note the red 2018 line is at the bottom of all these tracks. Most recently November 2018 is 0.50C lower than November 2016, and is the coolest November since 2011.
Summary
The oceans are driving the warming this century. SSTs took a step up with the 1998 El Nino and have stayed there with help from the North Atlantic, and more recently the Pacific northern "Blob." The ocean surfaces are releasing a lot of energy, warming the air, but eventually will have a cooling effect. The decline after 1937 was rapid by comparison, so one wonders: How long can the oceans keep this up? If the pattern of recent years continues, NH SST anomalies will likely cool in coming months. Once again, ENSO will probably determine the outcome.
Postscript:
In the most recent GWPF 2017 State of the Climate report, Dr. Humlum made this observation:
"It is instructive to consider the variation of the annual change rate of atmospheric CO2 together with the annual change rates for the global air temperature and global sea surface temperature (Figure 16). All three change rates clearly vary in concert, but with sea surface temperature rates leading the global temperature rates by a few months and atmospheric CO2 rates lagging 11–12 months behind the sea surface temperature rates."
Footnote: Why Rely on HadSST3
HadSST3 is distinguished from other SST products because HadCRU (Hadley Climatic Research Unit) does not engage in SST interpolation, i.e. infilling estimated anomalies into grid cells lacking sufficient sampling in a given month. From reading the documentation and from queries to Met Office, this is their procedure.
HadSST3 imports data from gridcells containing ocean, excluding land cells. From past records, they have calculated daily and monthly average readings for each grid cell for the period 1961 to 1990. Those temperatures form the baseline from which anomalies are calculated.
In a given month, each gridcell with sufficient sampling is averaged for the month and then the baseline value for that cell and that month is subtracted, resulting in the monthly anomaly for that cell. All cells with monthly anomalies are averaged to produce global, hemispheric and tropical anomalies for the month, based on the cells in those locations. For example, Tropics averages include ocean grid cells lying between latitudes 20N and 20S.
Gridcells lacking sufficient sampling that month are left out of the averaging, and the uncertainty from such missing data is estimated. IMO that is more reasonable than inventing data to infill. And it seems that the Global Drifter Array displayed in the top image is providing more uniform coverage of the oceans than in the past.

USS Pearl Harbor deploys Global Drifter Buoys in Pacific Ocean
from Climate Change Skeptic Blogs via hj on Inoreader http://bit.ly/2CsUXkW
No comments:
Post a Comment